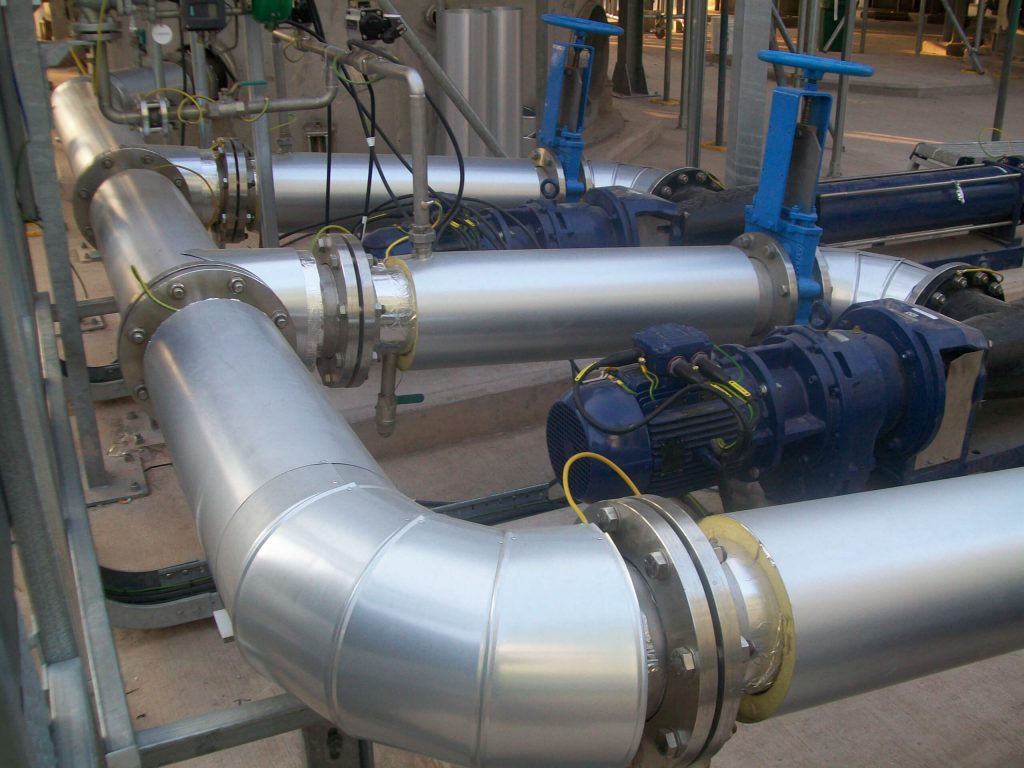
Thermal Insulation Types for the Industrial Sector
- Key Takeaways
- Understanding Thermal Insulation
- How Thermal Insulation Works
- Common Thermal Insulation Materials
- Specialised Insulation Types
- PIR Insulation and Insulation Methods
- Choosing the Right Insulation Material
- Installation Considerations
- Maintenance and Upkeep
- Benefits of Industrial Thermal Insulation
- Why Choose Thermal Clad?
- Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions
Thermal insulation is essential in industrial construction, reducing energy consumption, improving workplace comfort, and protecting buildings and equipment from extreme heat. Choosing the right insulation material can significantly impact operational costs, energy efficiency, and sustainability goals.
At Thermal Clad, we specialise in supplying and installing high-performance insulation systems for industrial, commercial, and mechanical applications. Drawing on our technical expertise and experience across sectors, we help clients identify the most effective insulation materials for their specific requirements.
In this article, we explore the most common thermal insulation types, how they work, and their applications across walls, floors, roofs, and industrial equipment.
Key Takeaways
- Thermal insulation types vary widely, including mineral wool, fibreglass, phenolic foam, and natural fibres, each suited to different industrial applications.
- Effective insulation reduces heat transfer, lowers energy costs, and supports environmental sustainability by minimising carbon footprint.
- Proper installation is crucial to prevent thermal bridging, air leakage, and moisture issues, ensuring optimal thermal resistance.
- Advanced options like PIR insulation, spray foam, and structural insulated panels offer high performance in limited spaces and complex industrial settings.
- Regular maintenance preserves insulation effectiveness, protecting equipment and improving workplace comfort and safety.
Understanding Thermal Insulation
Thermal insulation slows down the movement of heat between objects or within a building. Heat naturally flows from warmer areas to cooler areas, and this transfer occurs through conduction, convection, and radiation. Effective insulation materials disrupt this flow, helping to maintain stable temperatures and reduce energy use.
Industrial buildings often have complex heat management needs. From process equipment to storage areas, maintaining consistent internal temperatures protects machinery, prevents heat loss, and enhances safety. Thermal insulation is also vital for reducing a building’s carbon footprint, aligning operational efficiency with environmental sustainability.
How Thermal Insulation Works
At Thermal Clad, we use thermal insulation to insulate industrial services such as pipework and ductwork systems within factories and warehouses. The reason pipework and ductwork services are insulated can be explained by understanding how thermal insulation works. Thermal insulation works by forming a barrier that is created by the insulation material to resist heat transfer. Materials with low thermal conductivity, such as mineral wool, PIR boards, or closed-cell foams, prevent heat from moving not only through pipework and ductwork systems, but also through the building construction, such as through the walls, roofs, or floors. Insulation materials with a closed cell structure are particularly effective at blocking heat transfer and moisture, enhancing thermal efficiency and moisture resistance.
Thermal resistance, or R-value, is a key measurement that quantifies how effectively a material resists heat flow. Higher R-values indicate better insulation. Thickness is equally important: even small increases in insulation thickness can dramatically reduce heat loss in pipework and ductwork, which in turn prevents heat loss throughout the building construction.
Properly installed insulation also minimises thermal bridging, where gaps or inconsistencies allow heat to bypass the insulating layer. In industrial settings, this ensures that storage areas and production spaces remain energy-efficient and comfortable. In addition, this would help in industrial areas, where there may be close contact with machinery which is connected to hot exhaust flues, ductwork or pipework services. These services would require insulation to keep the outer surface of the services at a human-safe touch temperature.
Common Thermal Insulation Materials
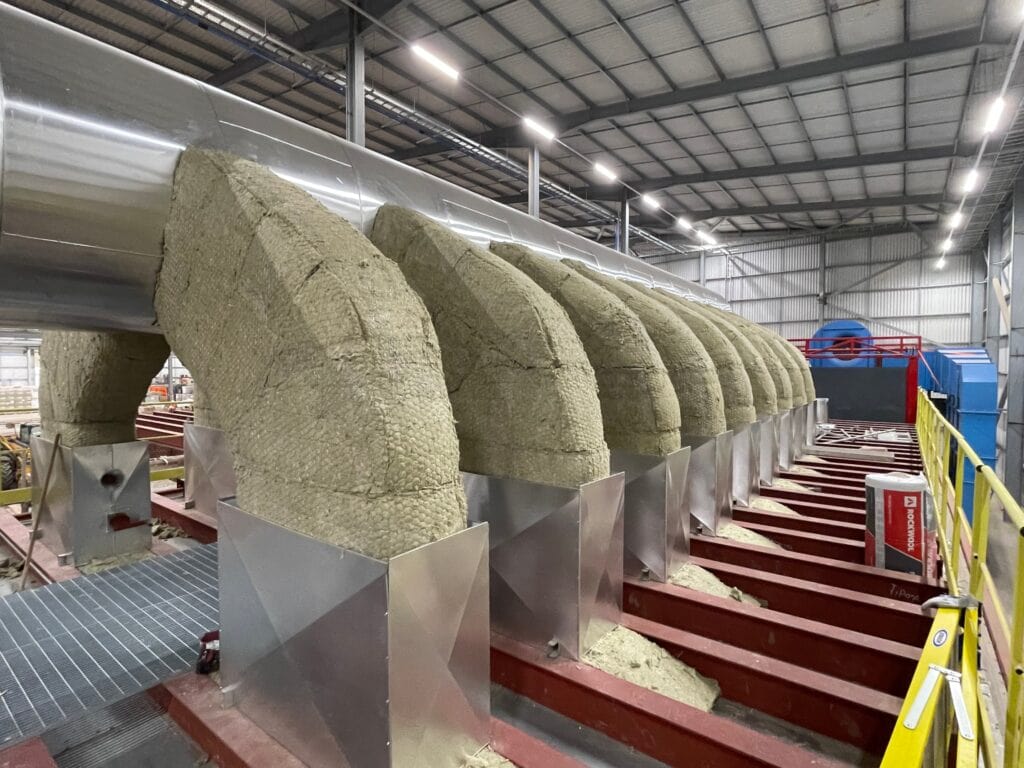

The industrial sector uses a variety of insulation materials, each with unique properties. These insulation materials are available in various forms, such as rolls, boards, and panels, to suit different applications. Such applications in an industrial setting may be ductwork and flues which can be installed with various shapes such as spiral, oval or rectangular. Understanding these options helps in selecting the right solution for specific applications.
Mineral Wool
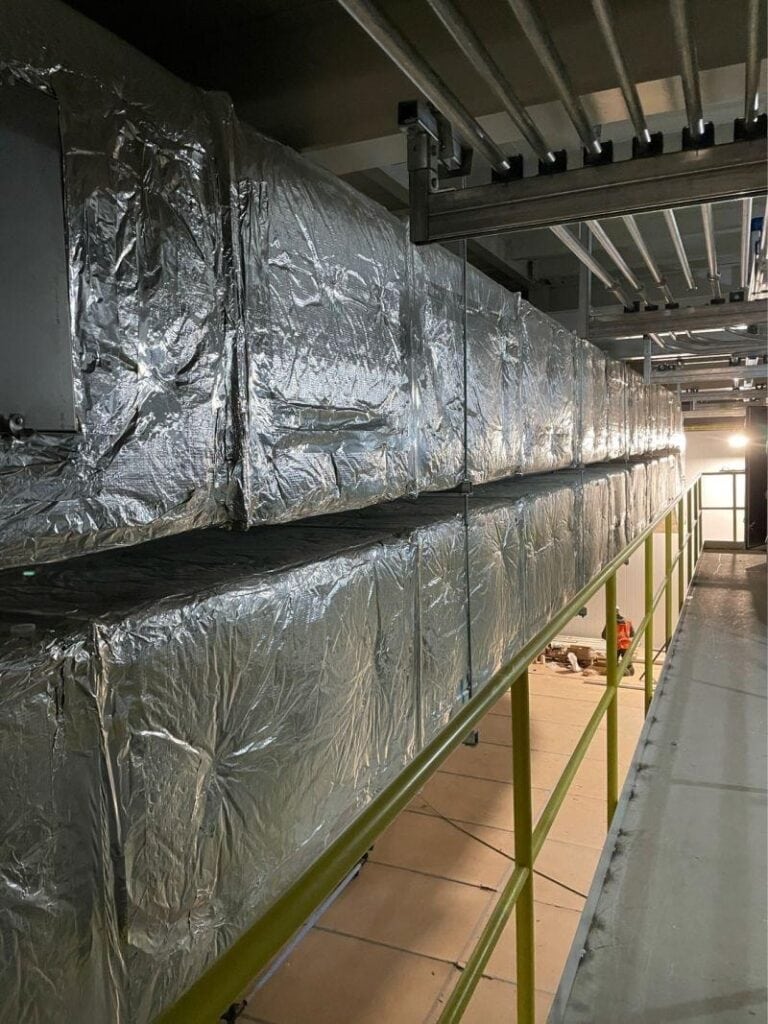

Mineral wool includes rock wool and glass wool. Rock wool is produced from volcanic basalt, offering durability, fire resistance, and excellent thermal performance. Glass wool, made from recycled glass, provides similar thermal resistance along with acoustic insulation benefits. While mineral wool is durable and provides fire resistance, it is generally not considered fully fire-resistant compared to some other insulation materials.
Thermal Clad would commonly use Mineral wool is commonly used in pipework and ductwork applications. It is typically available in the form of pipework sections, slabs, insulation boards or rolls, which makes installation easier and allows the material to fit efficiently onto the pipework and ductwork within the ceiling voids, floors or walls. Its fibrous structure traps air, creating effective thermal resistance while providing fire protection and soundproofing.
Fibreglass Insulation
Fibreglass insulation is made from fine strands of glass woven into mats or rolls. This material is widely used for walls, floors, and ceilings due to its low thermal conductivity, versatility, and fire resistance.
Fibreglass also provides acoustic insulation, reducing noise transmission in industrial environments. Its R-values within the UK vary by product from 0.032 to 0.044 W/mK (lambda value), resulting in an R value of approximately 2.25 to 2.4 per 100mm of thickness, making it suitable for many insulation projects. At the same thickness, fibreglass insulation can achieve similar thermal performance as some other insulation materials, depending on its density and composition.
Phenolic Foam
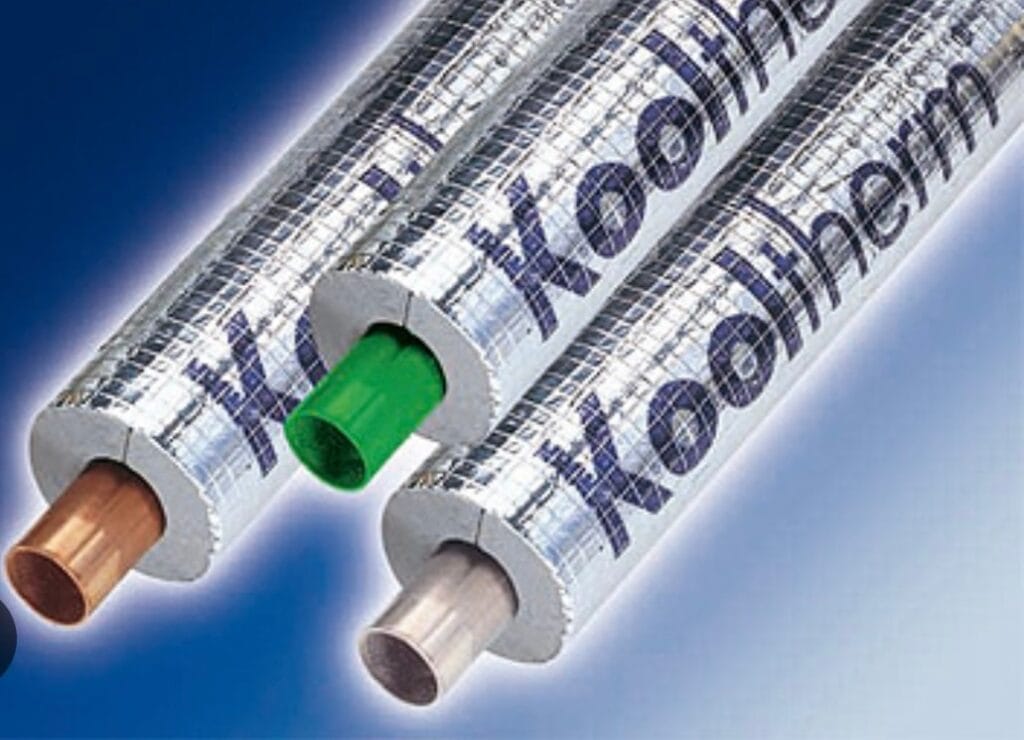

Phenolic foam is a high-performance material valued for its low thermal conductivity, moisture resistance, fire performance, and strength. It is widely applied in industrial settings, particularly for pipework, storage tanks, and process vessels.
With a low thermal conductivity (lambda value as low as 0.020 W/m-k), phenolic foam provides excellent insulation, which means insulation with a thinner profile can be installed, hence saving space, making it a reliable choice for laboratories, medical facilities, manufacturing facilities, and other industrial environments.
Specialised Insulation Types
Some industrial applications require specialised insulation designed for specific challenges. Other types of insulation, beyond the common options, may require professional installation or specialised techniques to ensure optimal performance.
PIR Insulation and Insulation Methods
Polyisocyanurate (PIR) insulation is a high-performance thermal insulation material widely used in modern construction. Thermal Clad mostly install PIR boards to externally located ductwork located in plant compounds or on flat roofs. This is the ductwork from heat recovery AHU systems, where keeping the warm air within the ductwork before it enters the building is important. With a rigid foam core and durable facings, PIR insulation delivers outstanding thermal resistance, making it a popular choice for external ductwork applications. Due to its closed cell structure, PIR is the ideal insulation for externally located ductwork, as when the weatherproof jacketing is applied onto it, it provides a hard-wearing, visually pleasant aesthetic finish.
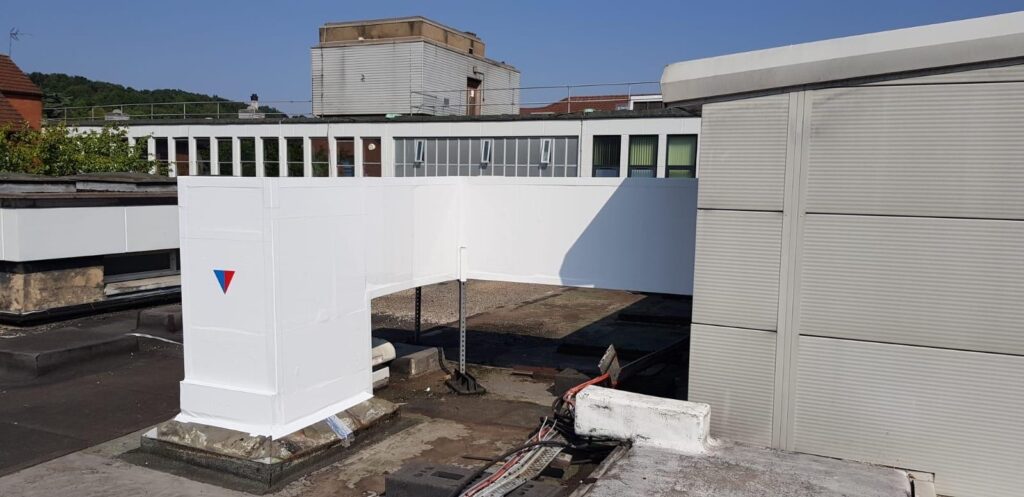

There are several methods for installing different types of insulation materials, each suited to specific building requirements. For example, fibreglass insulation is typically installed onto pipework and ductwork systems in sections, slabs or rolls between wall studs, ceiling voids or roof voids. Rigid foam sections or boards, such as Phenolic foam, are cut to fit and installed onto pipework and ductwork systems between structural elements to create a continuous insulating layer.
Regardless of the type of insulation or installation method, proper fitting is essential to maximise thermal resistance and prevent issues like thermal bridging, air leakage, or moisture accumulation. By choosing PIR insulation or other suitable materials and ensuring correct installation, building owners can achieve long-lasting energy efficiency and comfort.
Choosing the Right Insulation Material
Selecting insulation involves evaluating thermal conductivity, R-values, moisture tolerance, fire performance, environmental impact, and cost. Industrial projects may demand materials that resist extreme heat, provide fire protection, and offer long-term durability.
Rigid foam boards, like Phenolic or PIR insulation, provide high thermal resistance in thin layers, making them suitable for installation onto services where there is limited space. Mineral wool and fibreglass remain versatile choices for projects that also require acoustic insulation or a better level of fire resistance.
Environmental considerations are increasingly important. Recycled glass and natural fibres reduce embodied carbon, contributing to greener industrial facilities without compromising performance.
Installation Considerations
Correct installation is essential for insulation to perform as intended. Improper installation can lead to gaps, compression, or thermal bridging, which reduce energy efficiency.
Blanket and board insulation must be fitted carefully onto the pipework and ductwork, compressing the material. PIR and phenolic foam require professional application to ensure proper density and coverage.
Moisture control is vital. Vapour barriers, adequate ventilation, and selecting the correct type of insulation for the application is essential to avoid condensation and mould growth, maintaining the insulation’s thermal resistance over time.
By selecting the correct type of insulation for a construction, pipework and ductwork systems within the building will help with maintaining its energy efficiency and generally lowering the building’s carbon footprint, with the added advantage of helping the building occupants and owners save money on energy use and costs.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Regular inspections preserve insulation performance. Look for signs of moisture, damage, or settling that may reduce thermal resistance. Addressing issues promptly ensures consistent energy savings, reduces heat loss, and prolongs the life of insulation materials. Keeping regular maintenance of the insulating materials helps to keep the building and its services energy efficient.
In industrial settings, maintenance also involves ensuring that insulation continues to protect machinery, piping, and storage areas from extreme heat or cold. Routine checks can prevent costly repairs or downtime due to temperature-related issues.
Benefits of Industrial Thermal Insulation
Proper thermal insulation delivers multiple benefits:
- Reduced energy consumption and lower operational costs
- Stable indoor temperatures for comfort and safety
- Protection of equipment from heat stress
- Reduced carbon footprint and support for sustainability goals
- Fire resistance and moisture control for long-term durability
- When installed onto hot pipework and ductwork within industrial settings (such as kiln or oven duct), insulating materials can not only help keep the heat source within the duct, but also lower the external touch temperature, making it a suitable, safe temperature to touch for operatives who may come into contact with it. Therefore, insulation materials can play their part as an essential installation for health and safety reasons.
As there are various different types of insulating materials. By carefully selecting materials and installing them correctly, industrial facilities can achieve measurable energy efficiency improvements and create safer, more comfortable working environments.
Why Choose Thermal Clad?
We know you have options when it comes to insulation, but at Thermal Clad, we do things differently. Every project starts with a free consultation, giving you expert guidance from the very beginning. We take pride in our keen eye for detail, ensuring every system is installed to the highest standard for lasting thermal performance and the most suitable, cost-effective option.
Sustainability is at the heart of what we do. As an eco-friendly company, we prioritise materials and methods that help reduce energy use and support your environmental goals. We also understand that no two projects are the same, which is why we provide bespoke quotes tailored to your exact requirements, no one-size-fits-all pricing or assumptions.
With years of experience behind us, we’re recognised as industry experts in thermal insulation for industrial and commercial environments. Our work is backed by a quality assurance guarantee, giving you complete confidence that your insulation will perform as expected for years to come.
Speak to our team today to find out how we can help you design, supply, and install a system that delivers efficiency, reliability, and long-term value and using the right material.
Summary
Thermal insulation is a fundamental component of energy-efficient industrial buildings. From traditional materials like mineral wool and fibreglass to high-performance phenolic foam and PIR insulation boards, each option offers specific benefits.
Selecting the right material, ensuring proper installation, and maintaining insulation over time maximise energy efficiency, reduce heat loss, and lower operational costs. It also supports environmental responsibility by reducing carbon footprints and energy use.
Investing in high-quality thermal insulation contributes to safer, more sustainable, and cost-effective industrial operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Expert Guides
Our goal at Thermal Clad is to not only provide our customers with the finest service possible but also to keep them informed about new products and industry trends.
Please feel free to check out some of our expert insulation guides below:
Thermal Insulation Types for the Industrial Sector
Thermal insulation is essential in industrial construction, reducing energy consumption, improving workplace comfort, and protecting buildings and equipment from…
Cladding In Construction: What It Is And Its Purpose?
Cladding in construction refers to the process of covering insulated pipework, ducting, and vessels with a new layer of…
Pipe Insulation Benefits And Why It’s Important
Pipe insulation involves wrapping pipes with material to reduce heat loss and regulate temperature. This process helps maintain water…
Ductwork Insulation: Benefits & Guide
Duct insulation is essential for ensuring your HVAC systems operate efficiently by minimising temperature fluctuations during air transfer. It…
Heat Trace Cable: What Is It And How Does It Work?
Heat trace cables prevent pipes from freezing by generating heat. Curious about how heat trace cables work? This article…
Mistakes to Avoid When Insulating Your Pipework
Pipework insulation is a practical measure that offers many benefits in energy savings, freeze protection, condensation control, as well…
Expert Guide – Cladding Expertise
Various types of sheet metal cladding can be used to cover insulation. This protects against the elements and can…
4 Types of Materials Used in Thermal Insulation
The importance of choosing the right material for thermal insulation Thermal insulation is the reduction of the transfer of…
Rock Mineral Wool Insulation Vs Glass Wool Insulation
Rock Mineral Wool & Glass Wool Insulation Types: What are they and why should you choose them? Glass wool and Rock…